 Abstract:
Abstract:
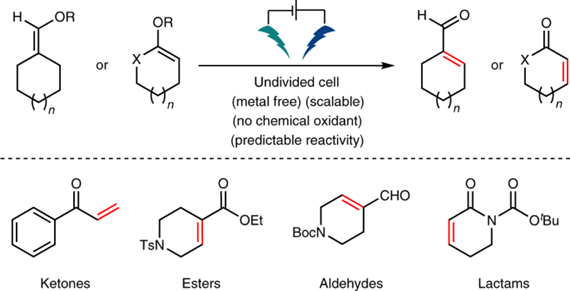
Electrochemical techniques have long been heralded for their innate sustainability as efficient methods to achieve redox reactions. Carbonyl desaturation, as a fundamental organic oxidation, is an oft-employed transformation to unlock adjacent reactivity through the formal removal of two hydrogen atoms. To date, the most reliable methods to achieve this seemingly trivial reaction rely on transition metals (Pd or Cu) or stoichiometric reagents based on I, Br, Se or S. Here we report an operationally simple pathway to access such structures from enol silanes and phosphates using electrons as the primary reagent. This electrochemically driven desaturation exhibits a broad scope across an array of carbonyl derivatives, is easily scalable (1–100 g) and can be predictably implemented into synthetic pathways using experimentally or computationally derived NMR shifts. Systematic comparisons to state-of-the-art techniques reveal that this method can uniquely desaturate a wide array of carbonyl groups. Mechanistic interrogation suggests a radical-based reaction pathway.
Access the full article now
Source
Graphical Abstract
Authors:
Samer Gnaim, Yusuke Takahira, Henrik R. Wilke, Zhen Yao, Jinjun Li, Dominique Delbrayelle, Pierre-Georges Echeverria, Julien C. Vantourout & Phil S. Baran
You may also ask to get in contact with our technical team through our contact form
Minakem Recherche, 145 Chemin des Lilas, 59310 Beuvry la Forêt, France
